Key Findings
- A typical American family with 4 telephones on a “household share” plan, paying $100 monthly for taxable wi-fi service would pay almost $320 per 12 months in taxes, charges, and authorities surcharges—up considerably from $294 in 2023.
- Nationally, taxes, charges, and authorities surcharges make up a record-high 26.8 p.c taxA tax is a compulsory fee or cost collected by native, state, and nationwide governments from people or companies to cowl the prices of normal authorities companies, items, and actions.
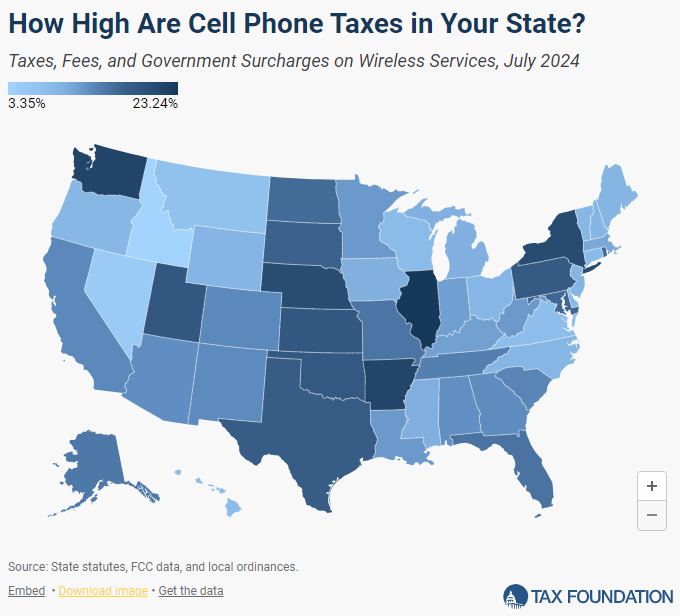
on taxable voice companies. Illinois residents proceed to have the very best wi-fi taxes within the nation at 36.0 p.c, adopted by Washington at 34.4 p.c and Arkansas at 34.2 p.c. Idaho residents pay the bottom wi-fi taxes at 16.1 p.c. - Oklahoma had the biggest improve of any state in 2024—from 26.9 p.c to 31.1 p.c—as a consequence of will increase within the 911 price and the State Common Service Fund cost.
- After lowering in 2023, the Federal Common Service Fund cost elevated considerably this 12 months from 10.8 p.c to 12.8 p.c. State and native taxes additionally elevated from 13.7 p.c to 14 p.c.
- The federal Everlasting Web Tax Freedom Act prevents state and native governments from imposing taxes and charges on wi-fi web entry. With out this federal prohibition, taxes and charges that apply to wi-fi voice companies may very well be utilized to web entry and considerably improve the tax burden on wi-fi payments.
- Since 2012, the common cost from wi-fi suppliers decreased by 29 p.c from $47.00 per line monthly to $33.56 per line. Nevertheless, throughout this identical time, wi-fi taxes, charges, and authorities surcharges elevated from 17.2 p.c to 26.8 p.c of the common invoice.
- Roughly 80 p.c of low-income adults and 75 p.c of all adults lived in wireless-only households. Wi-fi taxes are regressive and create important burdens on low-income households.
Introduction
Taxes and charges on the everyday American wi-fi shopper elevated considerably this 12 months from 24.5 p.c of a typical month-to-month invoice in 2023 to 26.8 p.c in 2024. This complete consists of state and native taxes averaging 14.0 p.c and the Federal Common Service Fund (FUSF) fee of 12.8 p.c.[1]
That is the fifteenth version of our report monitoring the taxes, charges, and authorities surcharges imposed on wi-fi voice companies by federal, state, and native governments. Our methodology stays constant. We examine the share charges of the taxes, charges, and authorities surcharges imposed on taxable wi-fi companies, referred to hereafter as “tax.” Flat fee impositions, corresponding to a $1.00 monthly per line 911 price, are transformed to a proportion utilizing the common month-to-month trade income per line as tracked by the Mobile Telecommunications and Web Affiliation (CTIA).
Over time, markets, product choices, and authorities insurance policies change. To include these modifications in our report, we additionally embody an alternate calculation. Federal regulation prohibits states from taxing web entry—together with information plans—and web entry makes up over half of the price of a median wi-fi shopper’s invoice. To point out how this limitation impacts tax collections and efficient tax charges, we calculate taxes paid as a proportion of each taxable and non-taxable companies. As information makes up a larger portion of our wi-fi consumption yearly, companies and merchandise supplied by wi-fi firms have tailored.
The wi-fi market has turn into more and more aggressive. The end result has been regular declines within the common value for wi-fi companies. Over roughly the final decade, the common month-to-month income per wi-fi line has fallen from $47.00 monthly to $33.56 monthly. Sadly, this value discount for customers has been partially offset by larger taxes.
There have been about 558 million wi-fi subscriber connections on the finish of 2023.[2] Wi-fi subscribers can pay roughly $12.4 billion in taxes, charges, and authorities surcharges to state and native governments in 2024 primarily based on the tax charges calculated on this report:
- $5.3 billion in gross sales taxes and different non-discriminatory consumption taxes that apply to different taxable items and companies
- $4.0 billion in state and native 911 and 988 charges, which incorporates a whole lot of thousands and thousands of {dollars} that aren’t truly used for 911 functions in some states
- $3.1 billion in further telecommunications-specific taxes
Wi-fi companies are sometimes the only real technique of communication and connectivity for Individuals, particularly youthful individuals and people with low incomes. In accordance with the Facilities for Illness Management and Prevention (CDC), about 80 p.c of all low-income adults lived in wireless-only households and 75 p.c of all adults lived in wireless-only households in 2023.[3] The $7.1 billion in state and native taxes and charges which are levied along with gross sales taxes disproportionately affect Individuals least capable of afford them.
Wi-fi Taxes and Charges Set a New Document Excessive in 2024
Taxes, charges, and authorities surcharges on wi-fi companies elevated to their highest degree ever, pushed by a rise within the FUSF fee and a rise in state and native taxes. The state and native burden elevated considerably, from 13.7 p.c to 14.0 p.c, whereas the FUSF surcharge fee elevated by two proportion factors, from 10.8 p.c to 12.8 p.c. Desk 1 highlights the modifications in wi-fi tax charges from 2003 to 2024.
Although the FUSF fee decreased in 2023, the speed of the FUSF surcharge has been rising steadily since 2017, and 2024 represents a continuation of that pattern. These FUSF fee will increase have been pushed by the decline within the value of telecommunications companies, mixed with the shift in shopper purchases from telecommunications companies to web entry. This pressured the Federal Communication Fee (FCC) to extend charges simply to maintain revenues fixed.
Determine 1 ranks the states from highest to lowest in wi-fi taxes, charges, and authorities surcharges. Illinois has the very best wi-fi taxes within the nation with state-local charges of almost 23 p.c. Washington, Arkansas, New York, and Nebraska spherical out the highest 5 states. Idaho, Nevada, and Montana have the bottom wi-fi taxes within the nation. The determine additionally maps the states by state/native tax charges. Excessive-tax states are distributed all through the nation, apart from the New England states, which are likely to have decrease charges.
Many states have debated whether or not to increase the gross sales taxA gross sales tax is levied on retail gross sales of products and companies and, ideally, ought to apply to all ultimate consumption with few exemptions. Many governments exempt items like groceries; base broadening, corresponding to together with groceries, may preserve charges decrease. A gross sales tax ought to exempt business-to-business transactions which, when taxed, trigger tax pyramiding.
base from tangible items to companies, with proponents of increasing the gross sales tax baseThe tax base is the overall quantity of revenue, property, belongings, consumption, transactions, or different financial exercise topic to taxation by a tax authority. A slender tax base is non-neutral and inefficient. A broad tax base reduces tax administration prices and permits extra income to be raised at decrease charges.
to companies arguing that the disparity in taxation between taxable tangible items and exempt companies doesn’t make sense. With regards to wi-fi companies, nonetheless, the precise reverse is true. As proven in Desk 2, wi-fi companies are topic to state and native taxes 1.8 instances larger than the gross sales taxes imposed on items, with the common state and native wi-fi tax fee of 14.0 p.c and the common mixed gross sales tax fee at about 7.8 p.c. In 17 states, wi-fi taxes are greater than twice as excessive as gross sales taxes. Three states which have chosen to not impose a gross sales tax—Delaware, Montana, and New Hampshire—have particular taxes on wi-fi and different telecommunications companies.
Whole Taxes Paid
Wi-fi customers can pay about $12.4 billion in taxes, charges, and authorities surcharges to state and native governments in 2024. Lower than half of this quantity—$5.3 billion—represents state and native gross sales and use taxes. These taxes are broadly utilized to taxable items and a few companies and don’t apply solely to wi-fi companies. The remaining $7.1 billion are taxes that apply solely to wi-fi and different telecommunications companies.
An in depth breakdown of the taxes, charges, and surcharges imposed by state and native governments in every state is offered within the Appendix. In lots of states, native authorities impositions range by particular person jurisdictions with some cities or unincorporated areas inside a state imposing no taxes and others imposing very excessive taxes. To facilitate interstate comparisons, native charges in probably the most populated metropolis and the capital metropolis in every state are averaged right into a single fee.
The Everlasting Web Tax Freedom Act prevents state and native governments from imposing taxes on web entry companies, together with wi-fi web entry. Information from the US Census Bureau means that greater than half of all wi-fi companies revenues are from web entry.[4] With out the safety of the federal regulation, the excessive excise taxAn excise tax is a tax imposed on a particular good or exercise. Excise taxes are generally levied on cigarettes, alcoholic drinks, soda, gasoline, insurance coverage premiums, amusement actions, and betting, and sometimes make up a comparatively small and risky portion of state and native and, to a lesser extent, federal tax collections.
charges utilized to taxable wi-fi companies may very well be utilized to web entry and shopper tax burdens could be considerably larger.
State Tendencies in Wi-fi Taxes
911 and 988 Charges
Most states impose per line charges on telecommunications prospects to fund capital and working bills for state and native emergency (911) methods. These charges range considerably, from zero in most counties in Missouri to a excessive of $5.00 per line in Chicago.[5] In 2024, Alabama, Connecticut, Nebraska, Ohio, Oklahoma, Pennsylvania, and South Dakota elevated 911 charges. The biggest will increase had been in South Dakota (from $1.25 per line monthly to $2.00 per line monthly) and Oklahoma (from $0.75 per line monthly to $1.25 per line monthly). West Virginia at present has the very best statewide wi-fi 911 price at $3.64 per line monthly.
In 2021, a brand new price started showing on buyer payments in three states. The FCC mandated {that a} new three-digit quantity (988) be designated nationally to contact suicide prevention hotlines that shall be operated within the states. A regulation handed by Congress approved states to impose “988 Charges” to pay for a few of the creation and operation of 988 disaster hotline facilities. In 2021, Virginia was the primary state to impose a brand new 988 price, which is 12 cents per line monthly. Since then, eight further states have enacted 988 charges on wi-fi customers. In 2024, Colorado lowered its 988 price from 27 cents per line to 14 cents per line. Delaware, Maryland, Minnesota, and Oregon carried out new 988 charges starting in 2024.
State Common Service Funds
Twenty-one states and Puerto Rico impose their very own State Common Service Fund (SUSF) expenses on wi-fi companies that present subsidies for lots of the identical functions because the FUSF. Beneath federal regulation, the federal authorities imposes a cost as a proportion of interstate revenues and states could impose a surcharge as a proportion of intrastate revenues. Just lately, nonetheless, some states have shifted to a per line SUSF imposition, which has resulted in a big portion of the SUSF burden being borne by wi-fi household share plans.
The remaining states proceed to impose their SUSF expenses on a proportion foundation. Texas made headlines in 2022 when the Public Utility Fee authorized a seven-fold improve within the SUSF fee, from 3.3 p.c to 24 p.c of intrastate expenses. A subsequent order decreased the speed to 12 p.c of intrastate expenses, which nonetheless resulted in a 350 p.c improve in SUSF surcharges on wi-fi buyer payments. Along with Texas, different states with excessive SUSF charges embody Arkansas at 8.3 p.c, adopted intently by Kansas (7.3 p.c) and Alaska (6.3 p.c). In 2024, Kansas, Kentucky, New Mexico, Oklahoma, and Utah elevated their SUSF expenses whereas Nevada and Wyoming decreased them.
State Wi-fi Taxes
Along with 911 charges, 988 charges, and SUSF expenses, 13 states impose wi-fi taxes which are both on prime of gross sales taxes or in lieu of gross sales taxes however at the next fee than the gross sales tax. Desk 4 exhibits these states by sort of wi-fi tax.
Native Wi-fi Taxes
Native governments all through the nation additionally impose taxes on wi-fi companies that aren’t imposed on different items and companies. Many of those taxes are imposed due to legacy taxes that had been established in the course of the regulated phone monopoly period that existed previous to the Nineteen Eighties breakup of AT&T. Native governments in some states have longstanding authority to impose right-of-way (ROW) charges on phone firms for putting poles, wires, and tools on native property. In different states, localities impose franchise or license taxes on phone firms in trade for the privilege of doing enterprise in a metropolis.
Within the late Nineteen Nineties and early 2000s, when wi-fi companies started to compete with wireline companies, localities grew to become involved about shedding revenues from native taxes on wireline phone firms and sought to increase these taxes to wi-fi companies. This occurred in some states although wi-fi suppliers sometimes didn’t use the general public right-of-way to put tools or, once they did use public property like on prime of buildings, the utilization was de minimis and paid for via negotiated rental agreements. This response to altering shopper conduct can be noticed in native taxation of streaming companies and cable firms, the place localities are combating to retain income by taxing streaming companies as in the event that they had been utilizing ROW like cable firms.[6]
Native governments in 14 states at present impose some sort of tax on wi-fi companies along with native choice gross sales taxes. In most of these states, the taxes are additive and solely additional improve the tax burden on wi-fi companies. California and Illinois are the exceptions—in these states, wi-fi companies are topic to taxes in lieu of the gross sales tax however most often the wi-fi tax is larger than the gross sales tax. Desk 4 gives a breakdown of the varieties of native wi-fi taxes that apply. Native taxes have a major affect on the general tax burden on wi-fi companies in a number of of the states with the very best wi-fi taxes, together with Illinois, Washington, Nebraska, New York, Utah, and Maryland.
California has the very best native taxes, with charges as much as 11 p.c. Washington follows intently with native taxes as excessive as 9 p.c, adopted by Illinois (as much as 7 p.c), Florida (as much as 7 p.c), and Nebraska (as much as 6.25 p.c). Along with these percentage-based taxes, Illinois permits native per line taxes of $5.00 per line in Chicago and Maryland permits Baltimore to cost $4.00 per line. Nebraska wi-fi customers will obtain some aid from excessive native taxes starting in October 2024, because the governor signed laws decreasing the cap on native wi-fi taxes from 6.25 p.c to 4 p.c.
The Regressive Affect of Wi-fi Taxes
Wi-fi companies taxes are regressive. Economists use the time period “regressive” to explain tax methods that impose larger tax burdens on low-income taxpayers than on higher-income taxpayers, as measured as a proportion of revenue. Low-income households pay a larger proportion of their budgets on wi-fi companies than high-income households. Subsequently, low-income households additionally pay a larger proportion of their budgets on wi-fi companies taxes.
The pattern of accelerating per-line impositions—for 911 charges, SUSF surcharges, and even per-line normal wi-fi taxes, together with the addition of 988 charges—makes wi-fi taxes much more regressive. Many consumption taxes have regressive results, and whereas that’s not in itself an argument in opposition to levying them, lawmakers must be cautious when rising regressive taxA regressive tax is one the place the common tax burden decreases with revenue. Low-income taxpayers pay a disproportionate share of the tax burden, whereas middle- and high-income taxpayers shoulder a comparatively small tax burden.
burdens, significantly within the case of a focused excise tax that doesn’t meaningfully internalize any exterior harms and infrequently far exceeds any quantity essential to pay for associated authorities applications.
Extreme taxes and charges improve the price of wi-fi companies at a time when residents are counting on wi-fi companies greater than ever for entry to authorities companies, together with schooling, well being care, distant work, and commerce. Actually, wi-fi companies have gotten the only real technique of communication and connectivity for a lot of Individuals, particularly these fighting poverty. About 80 p.c of all low-income adults had wireless-only service and 75 p.c of all adults had been wireless-only.
Desk 5 exhibits the affect of those excessive native taxes on wi-fi customers in chosen cities. In Chicago, a household of 4 paying $100 monthly for taxable wi-fi companies would pay about $34 monthly (over $400 per 12 months) in state and native taxes on wi-fi companies. That very same household in Baltimore would pay nearly $340 in state and native wi-fi taxes yearly.
Different Tax Comparisons
Wi-fi companies supplied to customers have modified dramatically since this report was first revealed in 2003. Once we first wrote the report, all parts of a shopper’s typical wi-fi invoice had been topic to tax, together with voice service, textual content messaging, information utilization, and associated ancillary companies in most states. At the moment, nonetheless, most wi-fi plans embody each taxable wi-fi companies in addition to non-taxable information plans used to entry the web. The federal Everlasting Web Tax Freedom Act prohibits state and native governments from imposing any taxes on web entry.
This part of the report presents various measures of the tax burden on wi-fi customers that account for the non-taxable web entry included in wi-fi plans. Common month-to-month income per wi-fi line is $33.56 monthly. Of this quantity, utilizing Census Bureau information, about 53.4 p.c of the everyday invoice is non-taxable web entry ($17.92 monthly) and the rest ($15.64 monthly) is taxable wi-fi companies.[7]
The primary column in Desk 6 ranks the states primarily based on the overall quantity of state and native tax paid on a typical shopper’s invoice. By this measure, Illinois nonetheless has the very best wi-fi tax burden within the nation, with the everyday shopper paying about $5.38 in state and native taxes monthly. Column two exhibits the efficient state and native tax fee as a proportion of the worth paid for the taxable wi-fi companies. As soon as once more, Illinois has the very best tax burden with the everyday shopper paying over one-third of the taxable portion in state and native taxes. The third column exhibits the efficient state and native tax fee as a share of the whole invoice, which incorporates each taxable and non-taxable companies. Even together with the non-taxable portion within the calculation, the efficient state and native tax fee is over 16 p.c in Illinois. Lastly, column 4 exhibits the efficient state and native tax fee utilizing the COST methodology that has historically been used on this report.
The declining portion of taxable companies could clarify why extra states have begun to rely extra closely on per-line taxes, charges, and authorities surcharges. For instance, whereas nearly each state imposes per-line 911 charges, extra states are shifting their SUSF impositions from a proportion of intrastate income to a flat, per-line quantity. California, Nebraska, New Mexico, Oklahoma, and Utah have all lately made this transformation in the previous few years and different states are contemplating it as nicely. Vermont will change from a proportion to a per-line imposition starting in 2025.
Beneath the choice comparisons in Desk 6, states that disproportionately depend on per-line taxes, corresponding to Illinois, Maryland, and West Virginia, have larger general tax rankings than states like California and Florida that rely predominately on percentage-based taxes. By their very nature, per-line taxes are regressive and have a tendency to burden lower-income wi-fi customers extra closely than percentage-based taxes. In addition they burden households as a result of most wi-fi suppliers cost much less per line for every further line added to a household plan. Whereas household and lower-income wi-fi customers bear the next burden, customers of higher-priced plans, usually enterprise customers, pay comparatively much less on a proportion foundation as a result of the per-line taxes signify a decrease relative price to the worth of their wi-fi plans.
The Financial Affect of Extreme Wi-fi Taxes
Policymakers must be cautious about increasing wi-fi taxes, charges, and authorities surcharges for 2 main causes. First, as mentioned above, wi-fi taxes are regressive and have a disproportionate affect on low-income customers. Extreme taxes and charges improve the price of entry to wi-fi companies for low-income customers at a time when lots of them depend on wi-fi as their solely telecommunications service.
Second, discriminatory taxes could sluggish funding in wi-fi infrastructure. Ample proof exists that investments in wi-fi networks present financial advantages to the broader economic system as a result of so many sectors—transportation, well being care, power, schooling, and even authorities—use wi-fi networks to spice up productiveness and effectivity. These financial advantages have confirmed particularly essential in the course of the COVID-19 pandemic as a result of wi-fi networks assist workers work remotely and permit college students to proceed their research.
Community funding is essential not solely to customers and companies that use these wi-fi networks but in addition to the whole American economic system. A report by the Worldwide Chamber of Commerce (ICC) surveyed the proof from the US, Europe, and the growing world, discovering that wi-fi infrastructure funding permits a complete entrepreneurial tradition to concentrate on creating functions and gadgets to make companies extra productive and to enhance the lives of customers. These instruments in flip make companies extra profitable in order that they’ll create new jobs that generate financial exercise and tax revenues for governments.
The ICC notes, “Remedying the discriminatory tax remedy of telecom items and companies could scale back tax receipts within the short-term, however the longer-term improve in using superior functionality gadgets, service demand, and community deployment ensuing from these tax reductions is prone to counteract this lack of income over time.”[8] Policymakers have to weigh the trade-offs between the short-term income advantages of extreme wi-fi taxes and the long-term financial affect on the state from decreased infrastructure funding.
Making use of the gross sales tax, a conventional broad-based consumption taxA consumption tax is usually levied on the acquisition of products or companies and is paid straight or not directly by the patron within the type of retail gross sales taxes, excise taxes, tariffs, value-added taxes (VAT), or an revenue tax the place all financial savings is tax-deductible.
, is completely applicable, however extreme focused taxation of wi-fi companies lacks the standard justifications—a “user-pays” system or the internalization of social prices—for excise taxation, elevating shopper prices and undercutting funding in a significant market.
Conclusion
Wi-fi customers proceed to be burdened with excessive taxes, charges, and authorities surcharges in lots of states and localities all through the nation. Properly over half of the $12.4 billion in state and native taxes imposed on wi-fi companies are discriminatory in nature, as they solely apply to telecommunications companies. These taxes disproportionately burden low-income Individuals and disincentivize funding in new wi-fi companies.
To alleviate the regressive affect on wi-fi customers, states ought to study their current communications tax constructions and contemplate insurance policies that transition their tax methods away from narrowly-based wi-fi taxes and towards broad-based tax sources that don’t distort the economic system and don’t sluggish funding in important infrastructure like wi-fi broadband.
Keep knowledgeable on the tax insurance policies impacting you.
Subscribe to get insights from our trusted consultants delivered straight to your inbox.
Subscribe
Appendix
Methodology
The methodology used on this report back to calculate wi-fi taxes compares the relevant federal, state, and native charges on wi-fi voice companies within the capital metropolis and probably the most populated metropolis in every state. This technique was developed by the Committee on State Taxation (COST) in its landmark “50-State Research and Report on Telecommunications Taxation,” first revealed in 2000.
The usage of a constant methodology permits for correct time-series comparisons throughout states and over time. Nevertheless, modifications in shopper demand for wi-fi companies pose challenges when measuring the affect of wi-fi taxes on shopper payments. Three tendencies within the trade are considerably impacting the quantity of taxes that wi-fi customers pay on their month-to-month payments.
First, a rising share of wi-fi shopper purchases is for web entry. US Census Bureau information from 2021 means that about 53.4 p.c of complete wi-fi companies revenues (which excludes gross sales and rental of apparatus and different non-service working income) for the trade are from the sale of web entry.[9] This proportion will proceed to develop as wi-fi customers make the most of extra web entry and fewer voice phone service annually.
Beneath federal regulation, as of July 1, 2020, all states are precluded from imposing taxes on web entry. This means that of the “typical” shopper’s month-to-month expenditure of $33.56 monthly, roughly $17.92 is for non-taxable web entry and $15.64 is for taxable wi-fi companies. A shopper making use of the tax charges on this report back to their complete invoice will discover that the efficient tax fee overstates their precise tax paid if their calling plan consists of each taxable voice companies and exempt web entry.
Second, the report’s methodology understates the tax fee affect of flat fee taxes and charges—these which are imposed as a set greenback quantity per line. Beneath the report’s methodology, a $1.00 monthly per line tax is transformed to a proportion quantity by dividing $1.00 by the $33.56 common month-to-month invoice, leading to a tax fee of three.0 p.c on this instance. Nevertheless, these flat fee taxes and charges are solely permitted to be imposed on the portion of the wi-fi invoice that’s not web entry. On this identical instance, if the $1.00 monthly had been divided by the taxable portion of the invoice ($15.64), the tax fee could be 6.4 p.c.
Third, the methodology for calculating the speed for the Federal Common Service Fund cost depends on using the FCC 37.1 p.c “secure harbor” for figuring out the share of a bundled companies plan that represents interstate telecommunications companies. Telecommunications suppliers have the choice of both utilizing the secure harbor proportion or a “visitors research” to find out the precise proportion of interstate revenues.
For the reason that visitors research sometimes ends in a decrease share of interstate revenues than the secure harbor proportion, wi-fi carriers use their very own visitors research which can lead to a decrease efficient fee for the FUSF than the speed calculated on this report. The report subsequently overstates considerably the speed of the FUSF. The report additionally understates the speed of the SUSF impositions since carriers should depend on the identical visitors research to calculate the intrastate portion of their revenues as a result of a visitors research that reduces assessable interstate revenues will improve assessable intrastate revenues.
Because of the modifications in product choices and shopper conduct, now we have included a piece on this 12 months’s report that gives various comparability methodologies that permit readers to grasp the affect of the web entry exemption on the efficient charges paid by wi-fi customers. This part can be useful when contemplating why lawmakers have routinely elevated charges on the taxable share of wi-fi companies.
Nevertheless, regardless of these altering behaviors and companies, the authors have decided that there are advantages to additionally retaining the present methodology, offering a constant measurement of tendencies in tax charges over time by persevering with to calculate the efficient tax fee for the taxable voice and textual content share of customers’ wi-fi payments as nicely.
What Are Common Service Funds?
The Federal Common Service Fund
The Federal Common Service Fund (FUSF) is run by the FCC below open-ended authority from Congress. This system subsidizes telecommunications companies for faculties, libraries, hospitals, low-income individuals, and rural phone firms working in high-cost areas. The FCC has additionally lately determined to make use of funds to subsidize broadband deployment.
The FCC has authority to set spending for these applications outdoors of the conventional congressional appropriations course of. After deciding what to spend on the varied applications, the FCC units the quarterly “contribution issue” or surcharge fee that telecommunications suppliers should remit to the FUSF to generate enough revenues to fund the expenditure commitments. Suppliers could elect to surcharge these “contributions” on their buyer payments.
FUSF surcharges apply solely to revenues from interstate telecommunications companies. They at present don’t apply to web entry service, data companies, and intrastate telecommunications companies.
Wi-fi carriers usually promote plans that embody both limitless voice minutes or a set variety of voice minutes for a set quantity. Since these plans embody each interstate calls (topic to the FUSF) and intrastate calls (not topic to FUSF), the FCC permits suppliers to allocate the mounted month-to-month plans to interstate and intrastate calls by considered one of two strategies. Carriers could use “visitors research” to point out the precise break up between interstate and interstate requires all subscribers and apply the FUSF to the aggregated interstate portion of subscriber calls.
Alternatively, carriers could use a single uniform nationwide “secure harbor” proportion to its mounted month-to-month plans. The FCC at present units this secure harbor at 37.1 p.c of the mounted month-to-month cost. For instance, when figuring out the FUSF, a $50 month-to-month wi-fi voice calling plan is deemed to incorporate $18.55 in interstate calls and $31.45 in intrastate calls. If a service elects to make use of the secure harbor, the FUSF fee could be utilized to $18.55 of the invoice every month.
The FUSF fee is ready by the FCC every quarter. For the interval starting July 1, 2024, the speed is 34.4 p.c. Thus, the FUSF fee utilized on assessable wi-fi revenues utilizing the FCC secure harbor quantity is 12.8 p.c (34.4 p.c instances 37.1 p.c).[10] Desk 7 highlights the numerous progress within the FCC contribution fee since 2003.
Regardless of the rising FUSF fee, Congress has proven little curiosity in proscribing or in any other case limiting the expansion of the applications funded via the FUSF or altering the methodology used to fund the FUSF applications. Nevertheless, current conflicting courtroom selections from a number of federal district courts concerning the legality of the FCC’s delegation of authority to manage the FUSF to a third-party company could power the FCC to re-open conversations about the way forward for the FUSF and the applications it funds.[11]
State Common Service Funds
States even have the authority to complement the applications funded via the FUSF with their very own applications funded via State Common Service Funds (SUSF). The state applications are funded by surcharges utilized to the intrastate portion of phone expenses. On this report, the inverse of the FUSF secure harbor is used to calculate the charges of the SUSF in all states besides Vermont, which imposes its SUSF on each interstate and intrastate expenses. As within the earlier instance, if a shopper has a $50 month-to-month wi-fi voice plan, 62.9 p.c of that cost ($31.45) is deemed to be an intrastate service topic to the SUSF cost and $18.55 is an interstate service not topic to SUSF expenses.
Just like the FUSF, SUSF expenses don’t apply to web entry. SUSF expenses are a key issue within the excessive wi-fi tax burden in states like Arkansas, Texas, Kansas, Alaska, Oklahoma, and Nebraska.
Footnotes
[1] This system subsidizes telecommunications companies for faculties, libraries, hospitals, low-income individuals, and rural phone firms working in high-cost areas. The calculation of the Federal Common Service Fund (FUSF) surcharge fee assumes that wi-fi suppliers use the “secure harbor” proportion. See the Appendix for a full clarification of the methodology.
[2] Determine consists of watches, tablets, and different related gadgets. Robert Roche, “CTIA’s Wi-fi Business Indices Report, Yr Finish 2022 Outcomes,” Mobile Telecommunications and Web Affiliation, July 2023.
[3] Stephen J. Blumberg and Julian V. Luke, “Wi-fi Substitution: Early Launch Estimates from the Nationwide Well being Interview Survey, July-December 2023,” Nationwide Middle for Well being Statistics, June 2024, https://www.cdc.gov/nchs/information/nhis/earlyrelease/wireless202406.pdf.
[4] US Census, 2022 Service Annual Survey, Desk 4, “Estimated Sources of Income for Employer Corporations, 2013 By 2022,” https://www2.census.gov/programs-surveys/sas/tables/time-series/sas-latest/Table4.xlsx.
[5] Missouri has no state 911 price on billed 911 service however does have a 911 price on pay as you go service.
[6] Ulrik Boesen, “Slicing the Wire from Cable Has States Courting New Income Streams,” Tax Basis, Jul. 19, 2021, https://taxfoundation.org/streaming-services-tax/.
[7] These figures are derived from US Census Bureau, 2022 Service Annual Survey, Desk 4, “Estimated Sources of Income for Employer Corporations, 2013 By 2022,” https://www2.census.gov/programs-surveys/sas/tables/time-series/sas-latest/Table4.xlsx.
[8] Worldwide Chamber of Commerce, “ICC Dialogue Paper on the Hostile Results of Discriminatory Taxes on Telecommunications Service,” Oct. 26, 2010, https://cdn.iccwbo.org/content/uploads/sites/3/2010/10/ICC-discussion-paper-on-the-adverse-effects-of-discriminatory-taxes-on-telecommunications-services.pdf.
[9] US Census Bureau, “Service Annual Survey Newest Information (NAICS-basis),” Desk 4, Nov. 23, 2021, https://www.census.gov/data/tables/2020/econ/services/sas-naics.html
[10] For the needs of this report, the FCC secure harbor proportion is used. This permits for constant multiyear comparisons of taxes, charges, and surcharges.
[11] Customers’ Analysis v. Federal Communications Fee, United States Courtroom of Appeals for the Fifth District (2024), https://www.ca5.uscourts.gov/opinions/pub/22/22-60008-CV2.pdf.
Share