The pandemic led to one of many largest fiscal responses in U.S. historical past, impacting households throughout the revenue distribution. A new report from the Congressional Funds Workplace (CBO) finds that these momentary insurance policies, together with different fixtures of our taxA tax is a compulsory cost or cost collected by native, state, and nationwide governments from people or companies to cowl the prices of basic authorities companies, items, and actions.
and switch system, diminished revenue inequality in 2020 by greater than every other 12 months since 1979 when the CBO started measuring family revenue. The evaluation additionally reveals that the federal tax system is markedly progressive, even when excluding the latest pandemic insurance policies, echoing our personal analysis on this subject and different latest academic evidence.
In response to the pandemic, policymakers considerably expanded employment compensation and issued restoration rebate credit (stimulus checks) to households. Collectively, the 2 insurance policies elevated revenue by greater than $800 billion, or greater than $6,000 per family on common. In distinction to different federal means-tested applications focused towards low-income households, expanded unemployment and stimulus checks benefited households throughout the distribution. Simply over half of the advantages went to the highest three quintiles. Nevertheless, as a share of revenue, the insurance policies had the most important profit for the underside quintile, representing greater than one-third of their incomes earlier than taxes and transfers. Laws additionally expanded Medicaid and the Supplemental Vitamin Help Program (SNAP), the 2 largest means-tested switch applications, additional boosting the incomes of households within the backside quintile.
On web, the insurance policies made the federal tax code extra redistributive and diminished revenue inequality to a 14-year low. The underside quintile noticed the most important features in revenue after taxes and transfers in comparison with 2019, rising by about 15 %. Since 1979, the underside quintile’s revenue has elevated by 126 %.
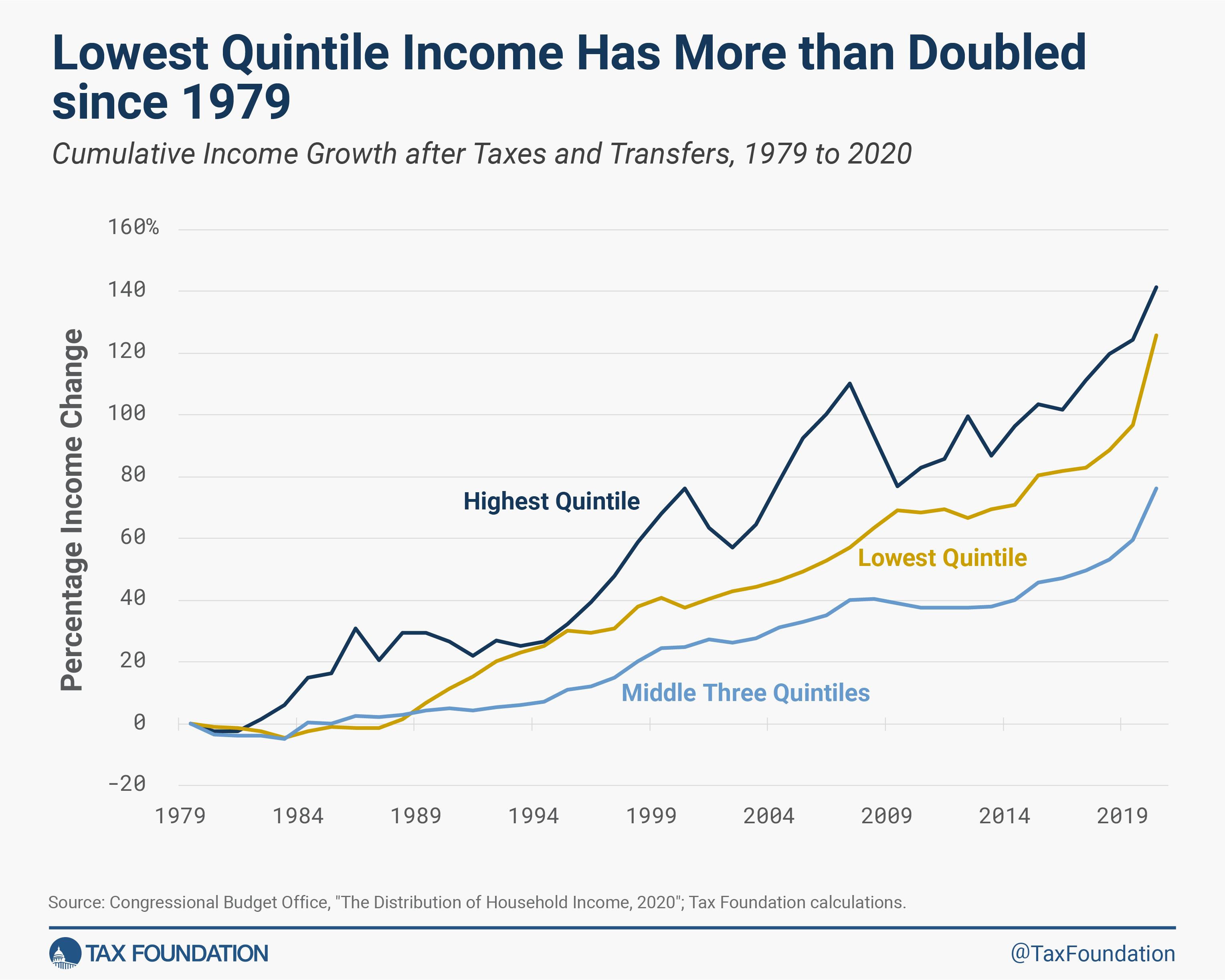
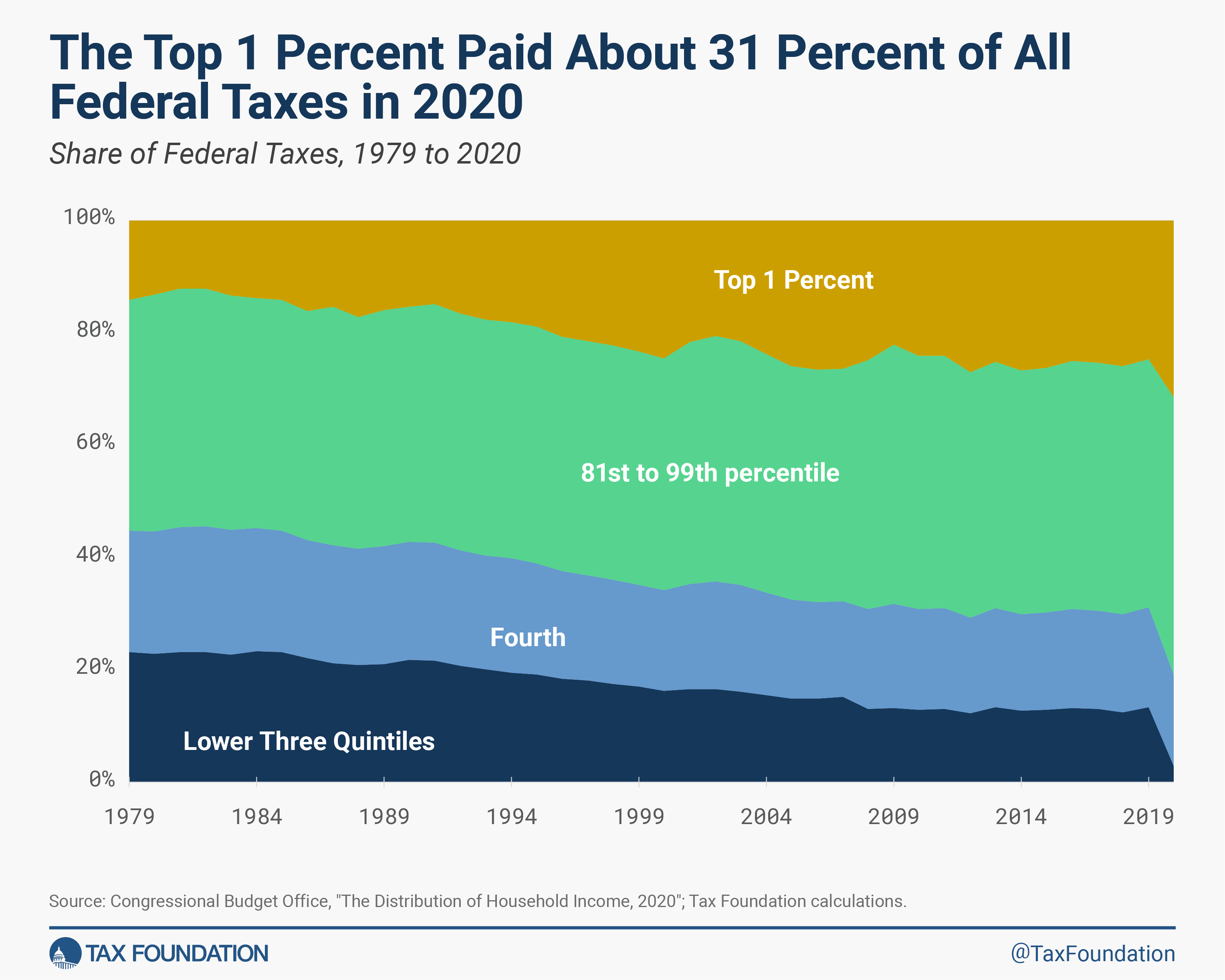
Excessive-income households proceed to pay a big share of federal taxes, together with particular person revenue taxes, payroll taxes, company taxes, and excise taxes. In 2020, the highest quintile earned about 56 % of all revenue, however paid 81 % of federal taxes—12 share factors greater than in 2019, regardless of incomes about the identical share of revenue. The highest 1 % of households alone paid 31 % of all federal taxes.
Common federal tax charges (inclusive of all particular person revenue, company, payroll, and excises taxes) barely modified for the highest quintile however declined notably for everybody else, principally as a result of restoration credit score rebates, which scale back tax liabilities. The underside quintile noticed its common tax feeThe typical tax fee is the whole tax paid divided by taxable revenue. Whereas marginal tax charges present the quantity of tax paid on the subsequent greenback earned, common tax charges present the general share of revenue paid in taxes.
fall by 17 share factors and change into unfavourable, that means households obtained extra in tax credit than they paid in taxes. Even with out the rebate restoration credit, the underside quintile would have confronted near zero in federal tax liabilities because of different credit and decrease pre-tax incomes extra usually.
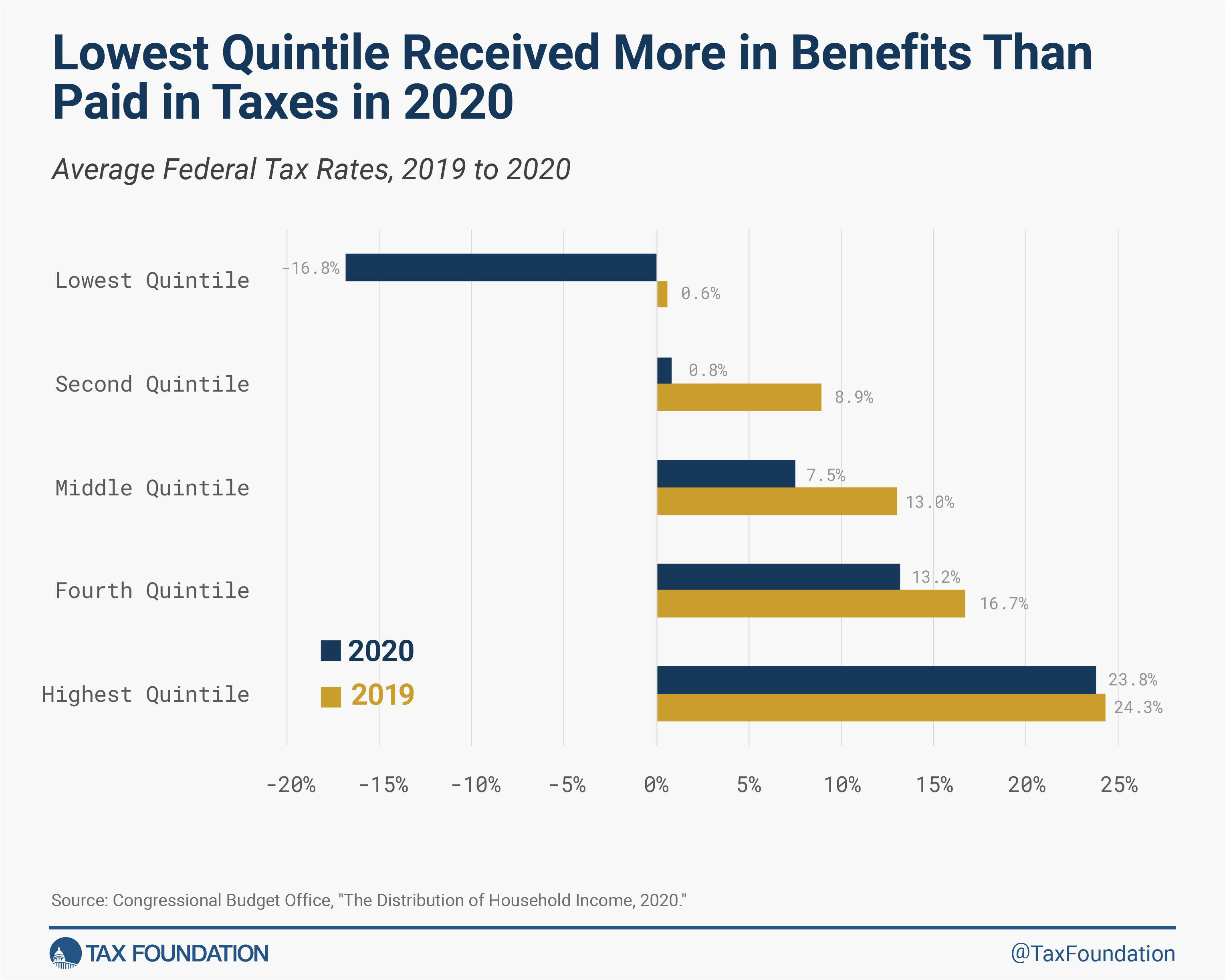
The general distribution of common tax charges, the place the highest quintile faces the most important burden and the burden declines for every subsequent quintile, signifies the U.S. federal tax and switch system is progressive. A latest tutorial paper affirmed this finding by trying not solely on the CBO knowledge but additionally two different measures of revenue constructed by Treasury economists and other academics. Although all three sources use totally different measures of revenue, all of them present that the “tax system has change into extra progressive and extra redistributive over the past a number of a long time, with a lot of that change occurring lately.” The rise in progressivity is primarily because of a rise in transfers to households within the backside half of the revenue distribution.
Altogether, the info introduced within the newest CBO report lends itself to 3 essential takeaways:
- COVID fiscal stimulus insurance policies considerably elevated incomes for individuals within the backside quintile.
- The COVID insurance policies made an already progressive federal tax and switch system much more progressive.
- The federal tax system continues to rely closely on high-income taxpayers to lift income.
Policymakers ought to preserve these details in thoughts as they proceed to debate how progressive our tax system ought to be and weigh the advantages and prices of increasing federal switch applications going ahead.
Keep knowledgeable on the tax insurance policies impacting you.
Subscribe to get insights from our trusted consultants delivered straight to your inbox.
Subscribe
Share
